- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
image from istockphoto
Hi Friends, We all know that the Indian Government make some changes in India's Tax Systems. In this topic, we will see What is GST? Why was GST implemented in India? Is GST is Right or Wrong for India? How GST is helpful for India's Tax System'? etc. discuss here. As we know that there are only 2 types of tax that are collected by the Indian Government. One is Direct Tax and the second is Indirect Tax. The government has only these 2 main sources of income.
 |
| image from istockphoto |
The meaning of Direct Tax is given by the government is that "The incident of tax and imposed of the tax is collected from the same person is know as Direct Tax." For example, some kind of tax amount is calculated on x person and the tax amount is collected from the x person this type of tax is a direct tax. There are many types of Direct Tax like Individual Income Tax, Corporate Income Tax, Capital Gain Tax, etc. are covered in Direct Tax.
 |
| image from istockphoto |
The meaning of Indirect Tax is given by the government is that "The incident of tax and assessed of the tax is collected from the other persons is known as Circular Tax." For example, The buyer of the product or service is given the price of goods and services in which a certain amount is added by the retailer & wholesaler, in that amount they add some profit and some amount of tax which is known as indirect tax. There are multiple types of Indirect Tax like Custom duty Tax, Service Tax, etc.,
Income source of Indian Government
As we discussed above the government have many ways to income source in which main sources are direct tax and indirect tax. which is collected by Central Government, or State Government.
Central Taxes:
Central Government has many types of taxes but the major source is direct tax and some minor sources are indirect tax. Direct tax is known as Income tax, Corporate tax, Capital Gain, and Security Transaction tax. And Indirect tax is known as Central Excise tax, Service tax, and Custom duty.
State Taxes:
State Government has many types of taxes but the major source is an indirect tax and some minor sources are direct tax. States Government has most important tax is known as Sales tax which is also known as "VAT TAX". The direct tax of state tax is only collected from Excise on alcohol.
Method of Tax Collection in India
Single Point Tax Collection
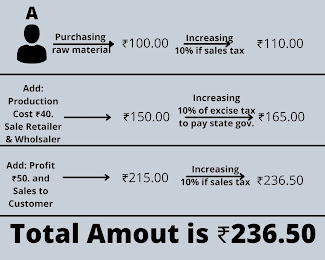
Before 1986 we are using the method to "Single Point Tax Collection". It means to collect tax amount in different stages but it doesn't matter that tax amount is calculated on the amount is including or not tax before it's calculated.
For example, If person A is purchases raw material of ₹100 on which sales tax is calculated 10% it means he has to pay a total of 110₹.
Then he produces the product with the help of raw material and he increased the amount to ₹40. That means the total price of the product is ₹150. After the production, he also has to pay an excise duty of 10% according to the government. so 150 is 10% is 15. Product price also increased by 15₹ which is 165₹.
The retailer or wholesaler's price is 165₹ and he included in profit behind the product is a minimum of ₹50 so it will become 215₹. And when he sale the product according to the state government act have to pay sales tax which is also 10%. Then the final and total price of the product has become 236.50₹.
The above-given example is related to Single Point Tax Collection. In this example, we found that tax is calculated on many different levels which are calculated sales tax on purchasing then excise tax calculated on production then again calculated sales tax on sales. This type of tax calculation is known as the "Cascading effect of Tax" we also say it "Tax on Tax".
Value Additional Tax
To solve this type of problem Government bring "Value Additional Tax" in 1986. Which is very useful for a country and states. To understand VAT let's see an example,
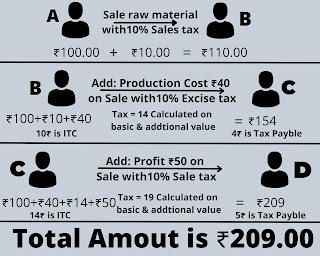
If Person A is sold to raw material Person B in ₹100 on which sales tax is calculated 10% it means he has to pay a total of 110₹.
So Person B purchased raw material in 110₹ [100₹+10₹]. Then Person B adds the value of production of ₹40 and sold to Person C then he has to pay an excise duty of 10% on value addition which is 14₹[100+40=140] So the total amount is ₹154. (note: In 110₹ ₹10 is tax so here tax calculated only 40₹ which is added and ₹10 is known as Input Tax Credit means the product person c is bought is already tax is paid. So when person c sold his product at ₹154 is included 14₹ of tax, out of this 14₹ we already pay ₹10 of Input Tax Credit that's why person c only pay 4₹ which is a different amount of tax. Here 14₹ is known as Output Tax Liability.)
In a simple world, Value Additional Tax means that Output Tax Liability is deducted from Input Tax Credit.
Then, Person C sold the product to Person D then again tax is not calculated on the total amount but tax is calculated on an amount which is added by Person C as a profit of ₹50. So the total price of the product is 190₹ [100+40+50](14₹ is tax amount.) and when he sold product sales tax calculated on product rate and the tax amount is ₹19. So total amount of product is ₹209 [190+19] (including this amount we already have an ITC of ₹14 so we have to pay only difference amount or amount which we add as profit to sale Person D and the tax amount is only ₹5.)
In a simple world "VAT = OTL - ITC"
where, OTL = Output Tax Liability,
ITC = Input Tax Credit.
Here we can see that the amount of tax and amount of the final product which is purchased through the consumer is very different between single point tax collection method or value additional tax. The difference amount in tax is 46.5₹ and the final product amount is also reduced. The difference amount benefit gets the consumer directly. So that we can say that if in single-point collection method any product tax rate is 12% and that same product rate in a vat has 18% is very better.
The central government has already adopted the 'VAT' method so they convince all states that they also adopt the same 'VAT' method to grow the revenue for the state but at starting many states are against adopting the method because they believe that if they adopting this method to grow the state so they will lose the revenue they got today. That's why after facing many problems central government convince all states to adopt the 'VAT' method. In 'VAT' method is a most useful benefit is that if there is a person 'A' person 'B' and person 'C' are in the chain then person B gets the benefit if person A pay his tax on time if person A failed to pay tax at a time then person B force person A for pay tax to get his ITC. at the same level if person B fails to pay tax Person C to force him to pay tax to get his ITC. With the help of this chain, they pay their tax on time. And also increase that to collect a tax of government.
After adopting the 'VAT' method some products on which consumers have to pay tax on tax means they have to still run cascading method some kind of goods like alcohols, that's types of drugs which are used for medical sources and the same method still exists in service tax method which government implements. According to the federal principle, there is a different rate between central and states government. If there is a different rate between central and state they never work as unity or a country. And that is the main point to come exist 'GST' and for adopting 'GST' there are also many points which are as under :
- Before adopting 'GST' there is a different rate between goods and services. After 1st July 2017, both services and goods both rate are same.
- Cenvat (Modvat) and VAT there is still cascading effect in this process. Where Cenvat is collected by the central government which is collected on production and VAT is collected by the State government which is collected on sales of products. To avoid this type of cascading effect on tax 'GST' is required.
- As well as there is also State Excise Duty and VAT they both are collected from the state government. Where state excise duty is collected on alcohol for the production of alcohol and VAT is collected on the sale of alcohol in this chain there is still exist cascading effect.
- In VAT there are different tax rates in different states. That's why one of the major point to implement 'GST' in India is to do an equal tax rate in all states. That government says 'One Nation One Tax".
- And Entry Tax and Octroi Tax which is paid in every states entry for transporting goods and etc.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps


Comments
Post a Comment